
Google Chrome is considered the most popular browser on most platforms and devices, including Apple, Android, and Windows. Browser Password Managers Examples # 1 Google Chrome In addition, there are no advanced features such as a data breach scanner, password health checker, etc. In fact, password managers in browsers have many shortcomings compared to full-blown password managers.įor example, built-in password tools do not support cross-platform browsing. It also syncs your data across devices as long as you use the same web browser.
#Firefox random password generator generator
Moreover, each browser-based password manager also provides a generator that creates strong passwords automatically. If you already have an account, you can save your passwords with only a single click. You do not need to download any file or register a new account. The first advantage of built-in password managers is their convenience. Let’s take a closer look at their pros and cons in the next paragraph! What are the Pros and Cons of Browser-based Password managers? If you choose to save the logins, the browser will fill out the credentials the next you visit these pages.
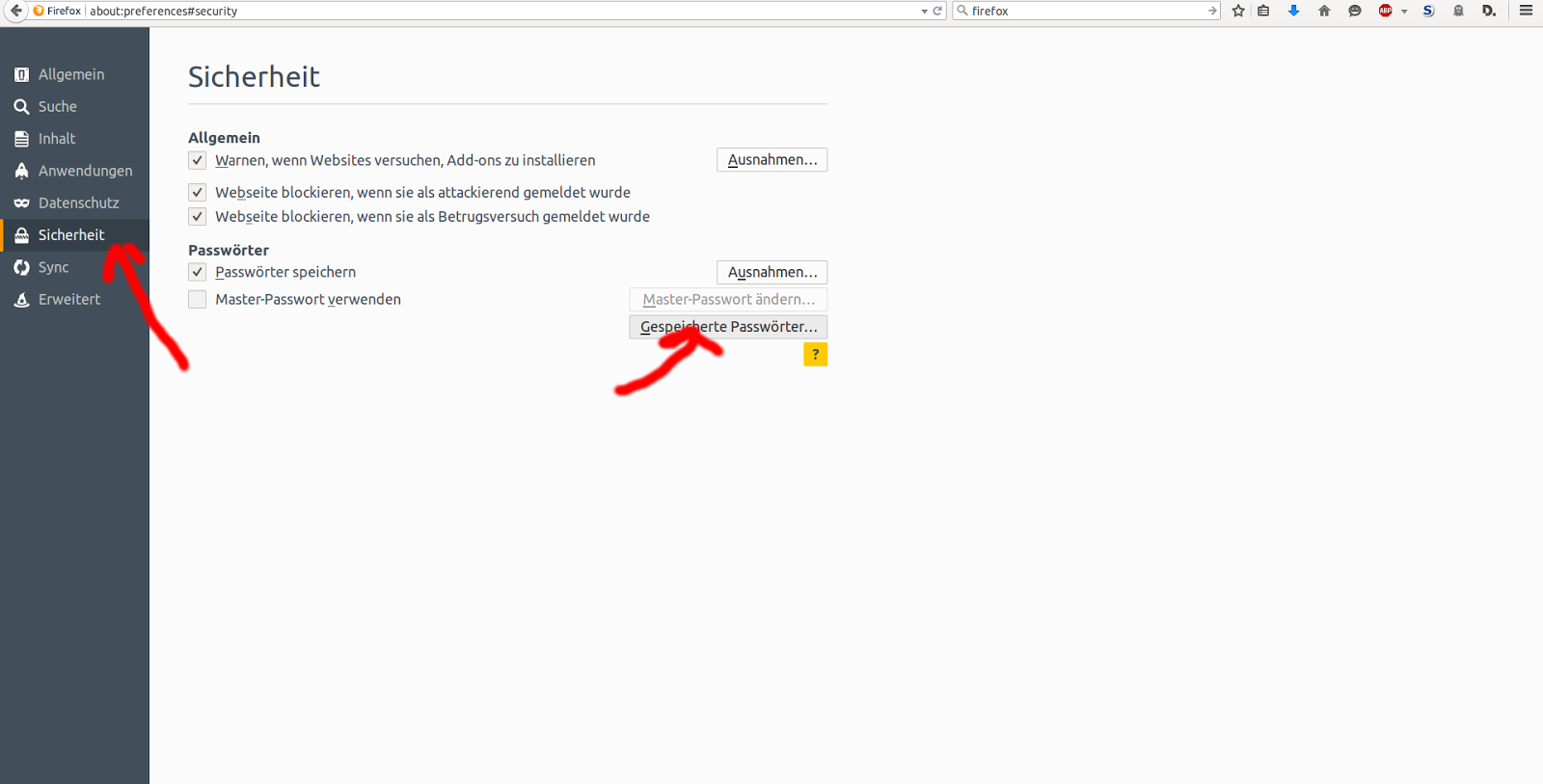
Your browser will automatically ask you if you want to keep your password every time you visit a new website that requires login details. Built-in password managers are available on all popular browsers

These tools are similar to standalone alternatives in terms of basic function. Google Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari, and Brave enable in-browser password management by default. What is a Browser-based Password Manager?
Then, let’s look over some examples to understand their features better. We’ll go over what browser-based password managers are all about, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Most browsers like Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Opera have a default password manager that allows users to save personal passwords for a seamless browsing experience. Comparing browser-based password managers: Is there any difference?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
